Main module (API)#
For more details regarding the main classes, see:
NNGT#
Package aimed at facilitating the analysis of Neural Networks and Graphs’ Topologies in Python by providing a unified interface for network generation and analysis.
The library mainly provides algorithms for
- generating networks
- studying their topological properties
- doing some basic spatial, topological, and statistical visualizations
- interacting with neuronal simulators and analyzing neuronal activity
Available modules#
- analysis
- Tools to study graph topology and neuronal activity.
- core
- Where the main classes are coded; however, most useful classes and methods for users are loaded at the main level (nngt) when the library is imported, so nngt.core should generally not be used.
- generation
- Functions to generate specific networks.
- geometry
- Tools to work on metric graphs (see PyNCulture).
- io
- Tools for input/output operations.
- lib
- Basic functions used by several most other modules.
- simulation
- Tools to provide complex network generation with NEST and help analyze the influence of the network structure on neuronal activity.
- plot
- Plot data or graphs using matplotlib.
nngt.Graph([nodes, name, weighted, …]) |
The basic graph class, which inherits from a library class such as graph_tool.Graph, networkx.DiGraph, or igraph.Graph. |
nngt.Group([nodes, properties, name]) |
Class defining groups of nodes. |
nngt.GroupProperty(size[, constraints, …]) |
Class defining the properties needed to create groups of neurons from an existing Graph or one of its subclasses. |
nngt.MetaGroup([nodes, name]) |
Class defining a meta-group of nodes. |
nngt.MetaNeuralGroup([nodes, name, properties]) |
Class defining a meta-group of neurons. |
nngt.Network([name, weighted, directed, …]) |
The detailed class that inherits from Graph and implements additional properties to describe various biological functions and interact with the NEST simulator. |
nngt.NeuralGroup([nodes, neuron_type, …]) |
Class defining groups of neurons. |
nngt.NeuralPop([size, parent, meta_groups, …]) |
The basic class that contains groups of neurons and their properties. |
nngt.SpatialGraph([nodes, name, weighted, …]) |
The detailed class that inherits from Graph and implements additional properties to describe spatial graphs (i.e. |
nngt.SpatialNetwork(population[, name, …]) |
Class that inherits from Network and SpatialGraph to provide a detailed description of a real neural network in space, i.e. |
nngt.Structure([size, parent, meta_groups]) |
The basic class that contains groups of nodes and their properties. |
nngt.generate(di_instructions, **kwargs) |
Generate a Graph or one of its subclasses from a dict containing all the relevant informations. |
nngt.get_config([key, detailed]) |
Get the NNGT configuration as a dictionary. |
nngt.load_from_file(filename[, fmt, …]) |
Load a Graph from a file. |
nngt.num_mpi_processes() |
Returns the number of MPI processes (1 if MPI is not used) |
nngt.on_master_process() |
Check whether the current code is executing on the master process (rank 0) if MPI is used. |
nngt.save_to_file(graph, filename[, fmt, …]) |
Save a graph to file. |
nngt.seed([msd, seeds]) |
Seed the random generator used by NNGT (i.e. |
nngt.set_config(config[, value, silent]) |
Set NNGT’s configuration. |
nngt.use_backend(backend[, reloading, silent]) |
Allows the user to switch to a specific graph library as backend. |
Details#
-
class
nngt.Graph(nodes=None, name='Graph', weighted=True, directed=True, copy_graph=None, structure=None, **kwargs)[source]# The basic graph class, which inherits from a library class such as
graph_tool.Graph,networkx.DiGraph, origraph.Graph.The objects provides several functions to easily access some basic properties.
Initialize Graph instance
Changed in version 2.0: Renamed from_graph to copy_graph.
Changed in version 2.2: Added structure argument.
Parameters: - nodes (int, optional (default: 0)) – Number of nodes in the graph.
- name (string, optional (default: “Graph”)) – The name of this
Graphinstance. - weighted (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the graph edges have weight properties.
- directed (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the graph is directed or undirected.
- copy_graph (
Graph, optional) – An optionalGraphthat will be copied. - structure (
Structure, optional (default: None)) – A structure dividing the graph into specific groups, which can be used to generate specific connectivities and visualise the connections in a more coarse-grained manner. - kwargs (optional keywords arguments) – Optional arguments that can be passed to the graph, e.g. a dict
containing information on the synaptic weights
(
weights={"distribution": "constant", "value": 2.3}which is equivalent toweights=2.3), the synaptic delays, or atypeinformation.
Note
When using copy_graph, only the topological properties are copied (nodes, edges, and attributes), spatial and biological properties are ignored. To copy a graph exactly, use
copy().Returns: self ( Graph)-
adjacency_matrix(types=False, weights=False, mformat='csr')[source]# Return the graph adjacency matrix.
Note
Source nodes are represented by the rows, targets by the corresponding columns.
Parameters: - types (bool, optional (default: False)) – Wether the edge types should be taken into account (negative values for inhibitory connections).
- weights (bool or string, optional (default: False)) – Whether the adjacecy matrix should be weighted. If True, all connections are multiply bythe associated synaptic strength; if weight is a string, the connections are scaled bythe corresponding edge attribute.
- mformat (str, optional (default: “csr”)) – Type of
scipy.sparsematrix that will be returned, by defaultscipy.sparse.csr_matrix.
Returns: mat (
scipy.sparsematrix) – The adjacency matrix of the graph.
-
edge_attributes# Access edge attributes.
-
static
from_file(filename, fmt='auto', separator=' ', secondary=';', attributes=None, attributes_types=None, notifier='@', ignore='#', from_string=False, name='LoadedGraph', directed=True, cleanup=False)[source]# Import a saved graph from a file.
Changed in version 2.0: Added optional attributes_types and cleanup arguments.
Parameters: - filename (str) – The path to the file.
- fmt (str, optional (default: deduced from filename)) – The format used to save the graph. Supported formats are:
“neighbour” (neighbour list), “ssp” (scipy.sparse), “edge_list”
(list of all the edges in the graph, one edge per line,
represented by a
source target-pair), “gml” (gml format, default if filename ends with ‘.gml’), “graphml” (graphml format, default if filename ends with ‘.graphml’ or ‘.xml’), “dot” (dot format, default if filename ends with ‘.dot’), “gt” (only when using graph_tool as library, detected if filename ends with ‘.gt’). - separator (str, optional (default ” “)) – separator used to separate inputs in the case of custom formats (namely “neighbour” and “edge_list”)
- secondary (str, optional (default: “;”)) – Secondary separator used to separate attributes in the case of custom formats.
- attributes (list, optional (default: [])) – List of names for the attributes present in the file. If a notifier is present in the file, names will be deduced from it; otherwise the attributes will be numbered. For “edge_list”, attributes may also be present as additional columns after the source and the target.
- attributes_types (dict, optional (default: str)) – Backup information if the type of the attributes is not specified in the file. Values must be callables (types or functions) that will take the argument value as a string input and convert it to the proper type.
- notifier (str, optional (default: “@”)) – Symbol specifying the following as meaningfull information.
Relevant information are formatted
@info_name=info_value, whereinfo_nameis in (“attributes”, “directed”, “name”, “size”) and associatedinfo_valueare of type (list,bool,str,int). Additional notifiers are@type=SpatialGraph/Network/SpatialNetwork, which must be followed by the relevant notifiers among@shape,@population, and@graph. - from_string (bool, optional (default: False)) – Load from a string instead of a file.
- ignore (str, optional (default: “#”)) – Ignore lines starting with the ignore string.
- name (str, optional (default: from file information or ‘LoadedGraph’)) – The name of the graph.
- directed (bool, optional (default: from file information or True)) – Whether the graph is directed or not.
- cleanup (bool, optional (default: False)) – If true, removes nodes before the first one that appears in the edges and after the last one and renumber the nodes from 0.
Returns: graph (
Graphor subclass) – Loaded graph.
-
classmethod
from_library(library_graph, name='ImportedGraph', weighted=True, directed=True, **kwargs)[source]# Create a
Graphby wrapping a graph object from one of the supported libraries.Parameters: - library_graph (object) – Graph object from one of the supported libraries (graph-tool, igraph, networkx).
- name (str, optional (default: “ImportedGraph”))
- **kwargs – Other standard arguments (see
__init__())
-
classmethod
from_matrix(matrix, weighted=True, directed=True, population=None, shape=None, positions=None, name=None)[source]# Creates a
Graphfrom ascipy.sparsematrix or a dense matrix.Parameters: - matrix (
scipy.sparsematrix ornumpy.ndarray) – Adjacency matrix. - weighted (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the graph edges have weight properties.
- directed (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the graph is directed or undirected.
- population (
NeuralPop) – Population to associate to the newNetwork. - shape (
Shape, optional (default: None)) – Shape to associate to the newSpatialGraph. - positions ((N, 2) array) – Positions, in a 2D space, of the N neurons.
- name (str, optional) – Graph name.
Returns: - matrix (
-
get_attribute_type(attribute_name, attribute_class=None)[source]# Return the type of an attribute (e.g. string, double, int).
Parameters: - attribute_name (str) – Name of the attribute.
- attribute_class (str, optional (default: both)) – Whether attribute_name is a “node” or an “edge” attribute.
Returns: type (str) – Type of the attribute.
-
get_betweenness(btype='both', weights=None)[source]# Returns the normalized betweenness centrality of the nodes and edges.
Parameters: - g (
Graph) – Graph to analyze. - btype (str, optional (default ‘both’)) – The centrality that should be returned (either ‘node’, ‘edge’, or ‘both’). By default, both betweenness centralities are computed.
- weights (bool or str, optional (default: binary edges)) – Whether edge weights should be considered; if
NoneorFalsethen use binary edges; ifTrue, uses the ‘weight’ edge attribute, otherwise uses any valid edge attribute required.
Returns: - nb (
numpy.ndarray) – The nodes’ betweenness if btype is ‘node’ or ‘both’ - eb (
numpy.ndarray) – The edges’ betweenness if btype is ‘edge’ or ‘both’
See also
- g (
-
get_degrees(mode='total', nodes=None, weights=None, edge_type='all')[source]# Degree sequence of all the nodes.
Changed in version 2.0: Changed deg_type to mode, node_list to nodes, use_weights to weights, and edge_type to edge_type.
Parameters: - mode (string, optional (default: “total”)) – Degree type (among ‘in’, ‘out’ or ‘total’).
- nodes (list, optional (default: None)) – List of the nodes which degree should be returned
- weights (bool or str, optional (default: binary edges)) – Whether edge weights should be considered; if
NoneorFalsethen use binary edges; ifTrue, uses the ‘weight’ edge attribute, otherwise uses any valid edge attribute required. - edge_type (int or str, optional (default: all)) – Restrict to a given synaptic type (“excitatory”, 1, or
“inhibitory”, -1), using either the “type” edge attribute for
non-
Networkor theinhibitorynodes.
Returns: - degrees (
numpy.array) - .. warning :: – When using MPI with “nngt” (distributed) backend, returns only the degrees associated to local edges. “Complete” degrees are obtained by taking the sum of the results on all MPI processes.
-
get_delays(edges=None)[source]# Returns the delays of all or a subset of the edges.
Changed in version 1.0.1: Added the possibility to ask for a subset of edges.
Parameters: edges ((E, 2) array, optional (default: all edges)) – Edges for which the type should be returned. Returns: the list of delays
-
get_density()[source]# Density of the graph:
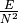 , where E is the number
of edges and N the number of nodes.
, where E is the number
of edges and N the number of nodes.
-
get_edge_attributes(edges=None, name=None)[source]# Attributes of the graph’s edges.
Changed in version 1.0: Returns the full dict of edges attributes if called without arguments.
New in version 0.8.
Parameters: - edge (tuple or list of tuples, optional (default:
None)) – Edge whose attribute should be displayed. - name (str, optional (default:
None)) – Name of the desired attribute.
Returns: - Dict containing all graph’s attributes (synaptic weights, delays…)
- by default. If edge is specified, returns only the values for these
- edges. If name is specified, returns value of the attribute for each
- edge.
Note
The attributes values are ordered as the edges in
edges_array()if edges is None.- edge (tuple or list of tuples, optional (default:
-
get_edge_types(edges=None)[source]# Return the type of all or a subset of the edges.
Changed in version 1.0.1: Added the possibility to ask for a subset of edges.
Parameters: edges ((E, 2) array, optional (default: all edges)) – Edges for which the type should be returned. Returns: the list of types (1 for excitatory, -1 for inhibitory)
-
get_edges(attribute=None, value=None, source_node=None, target_node=None)[source]# Return the edges in the network fulfilling a given condition.
Parameters: - attribute (str, optional (default: all nodes)) – Whether the attribute of the returned edges should have a specific value.
- value (object, optional (default : None)) – If an attribute name is passed, then only edges with attribute being equal to value will be returned.
- source_node (int or list of ints, optional (default: all nodes)) – Retrict the edges to those stemming from source_node.
- target_node (int or list of ints, optional (default: all nodes)) – Retrict the edges to those arriving at target_node.
See also
-
get_node_attributes(nodes=None, name=None)[source]# Attributes of the graph’s edges.
Changed in version 1.0.1: Corrected default behavior and made it the same as
get_edge_attributes().New in version 0.9.
Parameters: - nodes (list of ints, optional (default:
None)) – Nodes whose attribute should be displayed. - name (str, optional (default:
None)) – Name of the desired attribute.
Returns: - Dict containing all nodes attributes by default. If nodes is
- specified, returns a
dictcontaining only the attributes of these - nodes. If name is specified, returns a list containing the values of
- the specific attribute for the required nodes (or all nodes if
- unspecified).
See also
get_edge_attributes(),new_node_attribute(),set_node_attribute(),new_edge_attributes(),set_edge_attribute()- nodes (list of ints, optional (default:
-
get_nodes(attribute=None, value=None)[source]# Return the nodes in the network fulfilling a given condition.
Parameters: - attribute (str, optional (default: all nodes)) – Whether the attribute of the returned nodes should have a specific value.
- value (object, optional (default : None)) – If an attribute name is passed, then only nodes with attribute being equal to value will be returned.
See also
-
get_structure_graph()[source]# Return a coarse-grained version of the graph containing one node per
nngt.Group. Connections between groups are associated to the sum of all connection weights. If no structure is present, returns an empty Graph.
-
get_weights(edges=None)[source]# Returns the weights of all or a subset of the edges.
Changed in version 1.0.1: Added the possibility to ask for a subset of edges.
Parameters: edges ((E, 2) array, optional (default: all edges)) – Edges for which the type should be returned. Returns: the list of weights
-
graph# Returns the underlying library object.
Warning
Do not add or remove edges directly through this object.
-
is_connected(mode='strong')[source]# Return whether the graph is connected.
Parameters: mode (str, optional (default: “strong”)) – Whether to test connectedness with directed (“strong”) or undirected (“weak”) connections. References
[ig-connected] igraph - is_connected
-
is_network()[source]# Whether the graph is a subclass of
Network(i.e. if it has aNeuralPopattribute).
-
is_spatial()[source]# Whether the graph is embedded in space (i.e. is a subclass of
SpatialGraph).
-
static
make_network(graph, neural_pop, copy=False, **kwargs)[source]# Turn a
Graphobject into aNetwork, or aSpatialGraphinto aSpatialNetwork.Parameters: - graph (
GraphorSpatialGraph) – Graph to convert - neural_pop (
NeuralPop) – Population to associate to the newNetwork - copy (bool, optional (default:
False)) – Whether the operation should be made in-place on the object or if a new object should be returned.
Notes
In-place operation that directly converts the original graph if copy is
False, else returns the copiedGraphturned into aNetwork.- graph (
-
static
make_spatial(graph, shape=None, positions=None, copy=False)[source]# Turn a
Graphobject into aSpatialGraph, or aNetworkinto aSpatialNetwork.Parameters: - graph (
GraphorSpatialGraph) – Graph to convert. - shape (
Shape, optional (default: None)) – Shape to associate to the newSpatialGraph. - positions ((N, 2) array) – Positions, in a 2D space, of the N neurons.
- copy (bool, optional (default:
False)) – Whether the operation should be made in-place on the object or if a new object should be returned.
Notes
In-place operation that directly converts the original graph if copy is
False, else returns the copiedGraphturned into aSpatialGraph. The shape argument can be skipped if positions are given; in that case, the neurons will be embedded in a rectangle that contains them all.- graph (
-
name# Name of the graph.
-
neighbours(node, mode='all')[source]# Return the neighbours of node.
Parameters: - node (int) – Index of the node of interest.
- mode (string, optional (default: “all”)) – Type of neighbours that will be returned: “all” returns all the neighbours regardless of directionality, “in” returns the in-neighbours (also called predecessors) and “out” retruns the out-neighbours (or successors).
Returns: neighbours (set) – The neighbours of node.
-
new_edge_attribute(name, value_type, values=None, val=None)[source]# Create a new attribute for the edges.
Parameters: - name (str) – The name of the new attribute.
- value_type (str) – Type of the attribute, among ‘int’, ‘double’, ‘string’, or ‘object’
- values (array, optional (default: None)) – Values with which the edge attribute should be initialized. (must have one entry per node in the graph)
- val (int, float or str , optional (default: None)) – Identical value for all edges.
-
new_node_attribute(name, value_type, values=None, val=None)[source]# Create a new attribute for the nodes.
Parameters: - name (str) – The name of the new attribute.
- value_type (str) – Type of the attribute, among ‘int’, ‘double’, ‘string’, or ‘object’
- values (array, optional (default: None)) – Values with which the node attribute should be initialized. (must have one entry per node in the graph)
- val (int, float or str , optional (default: None)) – Identical value for all nodes.
-
node_attributes# Access node attributes.
-
set_delays(delay=None, elist=None, distribution=None, parameters=None, noise_scale=None)[source]# Set the delay for spike propagation between neurons.
Parameters: - delay (float or class:numpy.array, optional (default: None)) – Value or list of delays (for user defined delays).
- elist (class:numpy.array, optional (default: None)) – List of the edges (for user defined delays).
- distribution (class:string, optional (default: None)) – Type of distribution (choose among “constant”, “uniform”, “gaussian”, “lognormal”, “lin_corr”, “log_corr”).
- parameters (dict, optional (default: {})) – Dictionary containing the properties of the delay distribution.
- noise_scale (class:int, optional (default: None)) – Scale of the multiplicative Gaussian noise that should be applied on the delays.
-
set_edge_attribute(attribute, values=None, val=None, value_type=None, edges=None)[source]# Set attributes to the connections between neurons.
Warning
The special “type” attribute cannot be modified when using graphs that inherit from the
Networkclass. This is because for biological networks, neurons make only one kind of synapse, which is determined by thenngt.NeuralGroupthey belong to.Parameters: - attribute (str) – The name of the attribute.
- value_type (str) – Type of the attribute, among ‘int’, ‘double’, ‘string’
- values (array, optional (default: None)) – Values with which the edge attribute should be initialized. (must have one entry per node in the graph)
- val (int, float or str , optional (default: None)) – Identical value for all edges.
- value_type (str, optional (default: None)) – Type of the attribute, among ‘int’, ‘double’, ‘string’. Only used if the attribute does not exist and must be created.
- edges (list of edges or array of shape (E, 2), optional (default: all)) – Edges whose attributes should be set. Others will remain unchanged.
-
set_node_attribute(attribute, values=None, val=None, value_type=None, nodes=None)[source]# Set attributes to the connections between neurons.
Parameters: - attribute (str) – The name of the attribute.
- value_type (str) – Type of the attribute, among ‘int’, ‘double’, ‘string’
- values (array, optional (default: None)) – Values with which the edge attribute should be initialized. (must have one entry per node in the graph)
- val (int, float or str , optional (default: None)) – Identical value for all edges.
- value_type (str, optional (default: None)) – Type of the attribute, among ‘int’, ‘double’, ‘string’. Only used if the attribute does not exist and must be created.
- nodes (list of nodes, optional (default: all)) – Nodes whose attributes should be set. Others will remain unchanged.
-
set_types(edge_type, nodes=None, fraction=None)[source]# Set the synaptic/connection types.
Changed in version 2.0: Changed syn_type to edge_type.
Warning
The special “type” attribute cannot be modified when using graphs that inherit from the
Networkclass. This is because for biological networks, neurons make only one kind of synapse, which is determined by thenngt.NeuralGroupthey belong to.Parameters: - edge_type (int, string, or array of ints) – Type of the connection among ‘excitatory’ (also 1) or ‘inhibitory’ (also -1).
- nodes (int, float or list, optional (default: None)) – If nodes is an int, number of nodes of the required type that will be created in the graph (all connections from inhibitory nodes are inhibitory); if it is a float, ratio of edge_type nodes in the graph; if it is a list, ids of the edge_type nodes.
- fraction (float, optional (default: None)) – Fraction of the selected edges that will be set as edge_type (if nodes is not None, it is the fraction of the specified nodes’ edges, otherwise it is the fraction of all edges in the graph).
Returns: t_list (
numpy.ndarray) – List of the types in an order that matches the edges attribute of the graph.
-
set_weights(weight=None, elist=None, distribution=None, parameters=None, noise_scale=None)[source]# Set the synaptic weights.
Parameters: - weight (float or class:numpy.array, optional (default: None)) – Value or list of the weights (for user defined weights).
- elist (class:numpy.array, optional (default: None)) – List of the edges (for user defined weights).
- distribution (class:string, optional (default: None)) – Type of distribution (choose among “constant”, “uniform”, “gaussian”, “lognormal”, “lin_corr”, “log_corr”).
- parameters (dict, optional (default: {})) – Dictionary containing the properties of the weight distribution.
Properties are as follow for the distributions
- ‘constant’: ‘value’
- ‘uniform’: ‘lower’, ‘upper’
- ‘gaussian’: ‘avg’, ‘std’
- ‘lognormal’: ‘position’, ‘scale’
- noise_scale (class:int, optional (default: None)) – Scale of the multiplicative Gaussian noise that should be applied on the weights.
Note
If distribution and parameters are provided and the weights are set for the whole graph (elist is None), then the distribution properties will be kept as the new default for subsequent edges. That is, if new edges are created without specifying their weights, then these new weights will automatically be drawn from this previous distribution.
-
structure# Object structuring the graph into specific groups.
Note
Points to
populationif the graph is aNetwork.
-
to_file(filename, fmt='auto', separator=' ', secondary=';', attributes=None, notifier='@')[source]# Save graph to file; options detailed below.
See also
nngt.lib.save_to_file()function for options.
-
type# Type of the graph.
-
class
nngt.Group(nodes=None, properties=None, name=None, **kwargs)[source]# Class defining groups of nodes.
Its main variables are:
Variables: - ids –
listofintthe ids of the nodes in this group. - properties – dict, optional (default: {}) properties associated to the nodes
- is_metagroup –
boolwhether the group is a meta-group or not.
Note
A
Groupcontains a set of nodes that are unique; the size of the group is the number of unique nodes contained in the group. Passing non-unique nodes will automatically convert them to a unique set.Warning
Equality between
Group`s only compares the size and ``properties`attributes. This means that groups differing only by theiridswill register as equal.Calling the class creates a group of nodes. The default is an empty group but it is not a valid object for most use cases.
Parameters: - nodes (int or array-like, optional (default: None)) – Desired size of the group or, a posteriori, NNGT indices of the nodes in an existing graph.
- properties (dict, optional (default: {})) – Dictionary containing the properties associated to the nodes.
Returns: A new
Groupinstance.-
ids#
-
is_metagroup#
-
is_valid# i.e. if it has either a size or some ids associated to it.
Type: Whether the group can be used in a structure
-
name#
-
properties#
-
size#
- ids –
-
class
nngt.GroupProperty(size, constraints={}, neuron_model=None, neuron_param={}, syn_model=None, syn_param={})[source]# Class defining the properties needed to create groups of neurons from an existing
Graphor one of its subclasses.Variables: - size –
intSize of the group. - constraints –
dict, optional (default: {}) Constraints to respect when building theNeuralGroup. - neuron_model – str, optional (default: None) name of the model to use when simulating the activity of this group.
- neuron_param – dict, optional (default: {}) the parameters to use (if they differ from the model’s defaults)
Create a new instance of GroupProperties.
Notes
- The constraints can be chosen among:
- “avg_deg”, “min_deg”, “max_deg” (
int) to constrain the total degree of the nodes - “avg/min/max_in_deg”, “avg/min/max_out_deg”, to work with the in/out-degrees
- “avg/min/max_betw” (
double) to constrain the betweenness centrality - “in_shape” (
nngt.geometry.Shape) to chose neurons inside a given spatial region
- “avg_deg”, “min_deg”, “max_deg” (
Examples
>>> di_constrain = { "avg_deg": 10, "min_betw": 0.001 } >>> group_prop = GroupProperties(200, constraints=di_constrain)
- size –
-
class
nngt.MetaGroup(nodes=None, name=None, **kwargs)[source]# Class defining a meta-group of nodes.
Its main variables are:
Variables: ids – listofintthe ids of the nodes in this group.Calling the class creates a group of nodes. The default is an empty group but it is not a valid object for most use cases.
Parameters: - nodes (int or array-like, optional (default: None)) – Desired size of the group or, a posteriori, NNGT indices of the nodes in an existing graph.
- name (str, optional (default: “Group N”)) – Name of the meta-group.
Returns: A new
MetaGroupobject.
-
class
nngt.MetaNeuralGroup(nodes=None, name=None, properties=None, **kwargs)[source]# Class defining a meta-group of neurons.
Its main variables are:
Variables: Calling the class creates a group of neurons. The default is an empty group but it is not a valid object for most use cases.
Parameters: - nodes (int or array-like, optional (default: None)) – Desired size of the group or, a posteriori, NNGT indices of the neurons in an existing graph.
- name (str, optional (default: “Group N”)) – Name of the meta-group.
Returns: A new
MetaNeuralGroupobject.-
excitatory# Return the ids of all excitatory nodes inside the meta-group.
-
inhibitory# Return the ids of all inhibitory nodes inside the meta-group.
-
properties#
-
class
nngt.Network(name='Network', weighted=True, directed=True, from_graph=None, population=None, inh_weight_factor=1.0, **kwargs)[source]# The detailed class that inherits from
Graphand implements additional properties to describe various biological functions and interact with the NEST simulator.Initializes
Networkinstance.Parameters: - nodes (int, optional (default: 0)) – Number of nodes in the graph.
- name (string, optional (default: “Graph”)) – The name of this
Graphinstance. - weighted (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the graph edges have weight properties.
- directed (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the graph is directed or undirected.
- from_graph (
GraphObject, optional (default: None)) – An optionalGraphObjectto serve as base. - population (
nngt.NeuralPop, (default: None)) – An object containing the neural groups and their properties: model(s) to use in NEST to simulate the neurons as well as their parameters. - inh_weight_factor (float, optional (default: 1.)) – Factor to apply to inhibitory synapses, to compensate for example the strength difference due to timescales between excitatory and inhibitory synapses.
Returns: self (
Network)-
classmethod
exc_and_inhib(size, iratio=0.2, en_model='aeif_cond_alpha', en_param=None, in_model='aeif_cond_alpha', in_param=None, syn_spec=None, **kwargs)[source]# Generate a network containing a population of two neural groups: inhibitory and excitatory neurons.
Parameters: - size (int) – Number of neurons in the network.
- i_ratio (double, optional (default: 0.2)) – Ratio of inhibitory neurons:
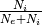 .
. - en_model (string, optional (default: ‘aeif_cond_alpha’)) – Nest model for the excitatory neuron.
- en_param (dict, optional (default: {})) – Dictionary of parameters for the the excitatory neuron.
- in_model (string, optional (default: ‘aeif_cond_alpha’)) – Nest model for the inhibitory neuron.
- in_param (dict, optional (default: {})) – Dictionary of parameters for the the inhibitory neuron.
- syn_spec (dict, optional (default: static synapse)) – Dictionary containg a directed edge between groups as key and the
associated synaptic parameters for the post-synaptic neurons (i.e.
those of the second group) as value. If provided, all connections
between groups will be set according to the values contained in
syn_spec. Valid keys are:
- (‘excitatory’, ‘excitatory’)
- (‘excitatory’, ‘inhibitory’)
- (‘inhibitory’, ‘excitatory’)
- (‘inhibitory’, ‘inhibitory’)
Returns: net (
Networkor subclass) – Network of disconnected excitatory and inhibitory neurons.See also
-
classmethod
from_gids(gids, get_connections=True, get_params=False, neuron_model='aeif_cond_alpha', neuron_param=None, syn_model='static_synapse', syn_param=None, **kwargs)[source]# Generate a network from gids.
Warning
Unless get_connections and get_params is True, or if your population is homogeneous and you provide the required information, the information contained by the network and its population attribute will be erroneous! To prevent conflicts the
to_nest()function is not available. If you know what you are doing, you should be able to find a workaround…Parameters: - gids (array-like) – Ids of the neurons in NEST or simply user specified ids.
- get_params (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the parameters should be obtained from NEST (can be very slow).
- neuron_model (string, optional (default: None)) – Name of the NEST neural model to use when simulating the activity.
- neuron_param (dict, optional (default: {})) – Dictionary containing the neural parameters; the default value will make NEST use the default parameters of the model.
- syn_model (string, optional (default: ‘static_synapse’)) – NEST synaptic model to use when simulating the activity.
- syn_param (dict, optional (default: {})) – Dictionary containing the synaptic parameters; the default value will make NEST use the default parameters of the model.
Returns: net (
Networkor subclass) – Uniform network of disconnected neurons.
-
get_edge_types()[source]# Return the type of all or a subset of the edges.
Changed in version 1.0.1: Added the possibility to ask for a subset of edges.
Parameters: edges ((E, 2) array, optional (default: all edges)) – Edges for which the type should be returned. Returns: the list of types (1 for excitatory, -1 for inhibitory)
-
get_neuron_type(neuron_ids)[source]# Return the type of the neurons (+1 for excitatory, -1 for inhibitory).
Parameters: neuron_ids (int or tuple) – NEST gids. Returns: ids (int or tuple) – Ids in the network. Same type as the requested gids type.
-
id_from_nest_gid(gids)[source]# Return the ids of the nodes in the
nngt.Networkinstance from the corresponding NEST gids.Parameters: gids (int or tuple) – NEST gids. Returns: ids (int or tuple) – Ids in the network. Same type as the requested gids type.
-
nest_gids#
-
neuron_properties(idx_neuron)[source]# Properties of a neuron in the graph.
Parameters: idx_neuron (int) – Index of a neuron in the graph. Returns: dict of the neuron’s properties.
-
set_types(edge_type, nodes=None, fraction=None)[source]# Set the synaptic/connection types.
Changed in version 2.0: Changed syn_type to edge_type.
Warning
The special “type” attribute cannot be modified when using graphs that inherit from the
Networkclass. This is because for biological networks, neurons make only one kind of synapse, which is determined by thenngt.NeuralGroupthey belong to.Parameters: - edge_type (int, string, or array of ints) – Type of the connection among ‘excitatory’ (also 1) or ‘inhibitory’ (also -1).
- nodes (int, float or list, optional (default: None)) – If nodes is an int, number of nodes of the required type that will be created in the graph (all connections from inhibitory nodes are inhibitory); if it is a float, ratio of edge_type nodes in the graph; if it is a list, ids of the edge_type nodes.
- fraction (float, optional (default: None)) – Fraction of the selected edges that will be set as edge_type (if nodes is not None, it is the fraction of the specified nodes’ edges, otherwise it is the fraction of all edges in the graph).
Returns: t_list (
numpy.ndarray) – List of the types in an order that matches the edges attribute of the graph.
-
to_nest(send_only=None, weights=True)[source]# Send the network to NEST.
See also
make_nest_network()for parameters
-
classmethod
uniform(size, neuron_model='aeif_cond_alpha', neuron_param=None, syn_model='static_synapse', syn_param=None, **kwargs)[source]# Generate a network containing only one type of neurons.
Parameters: - size (int) – Number of neurons in the network.
- neuron_model (string, optional (default: ‘aief_cond_alpha’)) – Name of the NEST neural model to use when simulating the activity.
- neuron_param (dict, optional (default: {})) – Dictionary containing the neural parameters; the default value will make NEST use the default parameters of the model.
- syn_model (string, optional (default: ‘static_synapse’)) – NEST synaptic model to use when simulating the activity.
- syn_param (dict, optional (default: {})) – Dictionary containing the synaptic parameters; the default value will make NEST use the default parameters of the model.
Returns: net (
Networkor subclass) – Uniform network of disconnected neurons.
-
class
nngt.NeuralGroup(nodes=None, neuron_type=1, neuron_model=None, neuron_param=None, name=None, **kwargs)[source]# Class defining groups of neurons.
Its main variables are:
Variables: - ids –
listofintthe ids of the neurons in this group. - neuron_type –
intthe default is1for excitatory neurons;-1is for inhibitory neurons; meta-groups must have neuron_type set toNone - neuron_model – str, optional (default: None) the name of the model to use when simulating the activity of this group
- neuron_param – dict, optional (default: {}) the parameters to use (if they differ from the model’s defaults)
- is_metagroup –
boolwhether the group is a meta-group or not (neuron_type isNonefor meta-groups)
Warning
Equality between
NeuralGroup`s only compares the size and neuronal type, ``model`andparamattributes. This means that groups differing only by theiridswill register as equal.Calling the class creates a group of neurons. The default is an empty group but it is not a valid object for most use cases.
Parameters: - nodes (int or array-like, optional (default: None)) – Desired size of the group or, a posteriori, NNGT indices of the neurons in an existing graph.
- neuron_type (int, optional (default: 1)) – Type of the neurons (1 for excitatory, -1 for inhibitory) or None if not relevant (only allowed for metag roups).
- neuron_model (str, optional (default: None)) – NEST model for the neuron.
- neuron_param (dict, optional (default: model defaults)) – Dictionary containing the parameters associated to the NEST model.
Returns: A new
NeuralGroupinstance.-
has_model#
-
ids#
-
nest_gids#
-
neuron_model#
-
neuron_param#
-
neuron_type#
-
properties#
- ids –
-
class
nngt.NeuralPop(size=None, parent=None, meta_groups=None, with_models=True, **kwargs)[source]# The basic class that contains groups of neurons and their properties.
Variables: - has_models –
bool,Trueif every group has amodelattribute. - size –
int, Returns the number of neurons in the population. - syn_spec –
dict, Dictionary containing informations about the synapses between the different groups in the population. - is_valid –
bool, Whether this population can be used to create a network in NEST.
Initialize NeuralPop instance.
Parameters: - size (int, optional (default: 0)) – Number of neurons that the population will contain.
- parent (
Network, optional (default: None)) – Network associated to this population. - meta_groups (dict of str/
NeuralGroupitems) – Optional set of groups. Contrary to the primary groups which define the population and must be disjoint, meta groups can overlap: a neuron can belong to several different meta groups. - with_models (
bool) – whether the population’s groups contain models to use in NEST - *args (items for OrderedDict parent)
- **kwargs (
dict)
Returns: pop (
NeuralPopobject.)-
add_to_group(group_name, ids)[source]# Add neurons to a specific group.
Parameters: - group_name (str or int) – Name or index of the group.
- ids (list or 1D-array) – Neuron ids.
-
create_group(neurons, name, neuron_type=1, neuron_model=None, neuron_param=None, replace=False)[source]# Create a new group in the population.
Parameters: - neurons (int or array-like) – Desired number of neurons or list of the neurons indices.
- name (str) – Name of the group.
- neuron_type (int, optional (default: 1)) – Type of the neurons : 1 for excitatory, -1 for inhibitory.
- neuron_model (str, optional (default: None)) – Name of a neuron model in NEST.
- neuron_param (dict, optional (default: None)) – Parameters for neuron_model in the NEST simulator. If None, default parameters will be used.
- replace (bool, optional (default: False)) – Whether to override previous exiting meta group with same name.
-
create_meta_group(neurons, name, neuron_param=None, replace=False)[source]# Create a new meta group and add it to the population.
Parameters: - neurons (int or array-like) – Desired number of neurons or list of the neurons indices.
- name (str) – Name of the group.
- neuron_type (int, optional (default: 1)) – Type of the neurons : 1 for excitatory, -1 for inhibitory.
- neuron_model (str, optional (default: None)) – Name of a neuron model in NEST.
- neuron_param (dict, optional (default: None)) – Parameters for neuron_model in the NEST simulator. If None, default parameters will be used.
- replace (bool, optional (default: False)) – Whether to override previous exiting meta group with same name.
-
classmethod
exc_and_inhib(size, iratio=0.2, en_model='aeif_cond_alpha', en_param=None, in_model='aeif_cond_alpha', in_param=None, syn_spec=None, parent=None, meta_groups=None)[source]# Make a NeuralPop with a given ratio of inhibitory and excitatory neurons.
Changed in version 0.8: Added syn_spec parameter.
Changed in version 1.2: Added meta_groups parameter
Parameters: size (int) – Number of neurons contained by the population.
iratio (float, optional (default: 0.2)) – Fraction of the neurons that will be inhibitory.
en_model (str, optional (default: default_neuron)) – Name of the NEST model that will be used to describe excitatory neurons.
en_param (dict, optional (default: default NEST parameters)) – Parameters of the excitatory neuron model.
in_model (str, optional (default: default_neuron)) – Name of the NEST model that will be used to describe inhibitory neurons.
in_param (dict, optional (default: default NEST parameters)) – Parameters of the inhibitory neuron model.
syn_spec (dict, optional (default: static synapse)) – Dictionary containg a directed edge between groups as key and the associated synaptic parameters for the post-synaptic neurons (i.e. those of the second group) as value. If provided, all connections between groups will be set according to the values contained in syn_spec. Valid keys are:
- (‘excitatory’, ‘excitatory’)
- (‘excitatory’, ‘inhibitory’)
- (‘inhibitory’, ‘excitatory’)
- (‘inhibitory’, ‘inhibitory’)
parent (
Network, optional (default: None)) – Network associated to this population.meta_groups (list dict of str/
NeuralGroupitems) – Additional set of groups which can overlap: a neuron can belong to several different meta groups. Contrary to the primary ‘excitatory’ and ‘inhibitory’ groups, meta groups are therefore no necessarily disjoint. If all meta-groups have a name, they can be passed directly through a list; otherwise a dict is necessary.
See also
nest.Connect(),as()
-
excitatory# Return the ids of all excitatory nodes inside the population.
New in version 1.3.
-
classmethod
from_groups(groups, names=None, syn_spec=None, parent=None, meta_groups=None, with_models=True)[source]# Make a NeuralPop object from a (list of)
NeuralGroupobject(s).Parameters: - groups (list of
NeuralGroupobjects) – Groups that will be used to form the population. Note that a given neuron can only belong to a single group, so the groups should form pairwise disjoints complementary sets. - names (list of str, optional (default: None)) – Names that can be used as keys to retreive a specific group. If not provided, keys will be the group name (if not empty) or the position of the group in groups, stored as a string. In the latter case, the first group in a population named pop will be retreived by either pop[0] or pop[‘0’].
- parent (
Graph, optional (default: None)) – Parent if the population is created from an exiting graph. - syn_spec (dict, optional (default: static synapse)) – Dictionary containg a directed edge between groups as key and the associated synaptic parameters for the post-synaptic neurons (i.e. those of the second group) as value. If a ‘default’ entry is provided, all unspecified connections will be set to its value.
- meta_groups (list or dict of str/
NeuralGroupitems) – Additional set of groups which can overlap: a neuron can belong to several different meta groups. Contrary to the primary groups, meta groups do therefore no need to be disjoint. If all meta-groups have a name, they can be passed directly through a list; otherwise a dict is necessary. - with_model (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the groups require models (set to False to use populations for graph theoretical purposes, without NEST interaction)
Example
For synaptic properties, if provided in syn_spec, all connections between groups will be set according to the values. Keys can be either group names or types (1 for excitatory, -1 for inhibitory). Because of this, several combination can be available for the connections between two groups. Because of this, priority is given to source (presynaptic properties), i.e. NNGT will look for the entry matching the first group name as source before looking for entries matching the second group name as target.
# we created groups `g1`, `g2`, and `g3` prop = { ('g1', 'g2'): {'model': 'tsodyks2_synapse', 'tau_fac': 50.}, ('g1', g3'): {'weight': 100.}, ... } pop = NeuronalPop.from_groups( [g1, g2, g3], names=['g1', 'g2', 'g3'], syn_spec=prop)
Note
If the population is not generated from an existing
Graphand the groups do not contain explicit ids, then the ids will be generated upon population creation: the first group, of size N0, will be associated the indices 0 to N0 - 1, the second group (size N1), will get N0 to N0 + N1 - 1, etc.- groups (list of
-
classmethod
from_network(graph, *args)[source]# Make a NeuralPop object from a network. The groups of neurons are determined using instructions from an arbitrary number of
GroupProperties.
-
get_param(groups=None, neurons=None, element='neuron')[source]# Return the element (neuron or synapse) parameters for neurons or groups of neurons in the population.
Parameters: - groups (
str,intor array-like, optional (default:None)) – Names or numbers of the groups for which the neural properties should be returned. - neurons (int or array-like, optional (default:
None)) – IDs of the neurons for which parameters should be returned. - element (
listofstr, optional (default:"neuron")) – Element for which the parameters should be returned (either"neuron"or"synapse").
Returns: param (
list) – List of all dictionaries with the elements’ parameters.- groups (
-
has_models#
-
inhibitory# Return the ids of all inhibitory nodes inside the population.
New in version 1.3.
-
nest_gids# Return the NEST gids of the nodes inside the population.
New in version 1.3.
-
set_model(model, group=None)[source]# Set the groups’ models.
Parameters: - model (dict) – Dictionary containing the model type as key (“neuron” or “synapse”) and the model name as value (e.g. {“neuron”: “iaf_neuron”}).
- group (list of strings, optional (default: None)) – List of strings containing the names of the groups which models should be updated.
Note
By default, synapses are registered as “static_synapse”s in NEST; because of this, only the
neuron_modelattribute is checked by thehas_modelsfunction: it will answerTrueif all groups have a ‘non-None’neuron_modelattribute.Warning
No check is performed on the validity of the models, which means that errors will only be detected when building the graph in NEST.
-
set_neuron_param(params, neurons=None, group=None)[source]# Set the parameters of specific neurons or of a whole group.
New in version 1.0.
Parameters: - params (dict) – Dictionary containing parameters for the neurons. Entries can be either a single number (same for all neurons) or a list (one entry per neuron).
- neurons (list of ints, optional (default: None)) – Ids of the neurons whose parameters should be modified.
- group (list of strings, optional (default: None)) – List of strings containing the names of the groups whose parameters should be updated. When modifying neurons from a single group, it is still usefull to specify the group name to speed up the pace.
Note
If both neurons and group are None, all neurons will be modified.
Warning
No check is performed on the validity of the parameters, which means that errors will only be detected when building the graph in NEST.
-
syn_spec# The properties of the synaptic connections between groups. Returns a
dictcontaining tuples as keys and dicts of parameters as values.The keys are tuples containing the names of the groups in the population, with the projecting group first (presynaptic neurons) and the receiving group last (post-synaptic neurons).
Example
For a population of excitatory (“exc”) and inhibitory (“inh”) neurons.
syn_spec = { ("exc", "exc"): {'model': 'stdp_synapse', 'weight': 2.5}, ("exc", "inh"): {'model': 'static_synapse'}, ("exc", "inh"): {'model': 'stdp_synapse', 'delay': 5.}, ("inh", "inh"): { 'model': 'stdp_synapse', 'weight': 5., 'delay': ('normal', 5., 2.)} } }
New in version 0.8.
-
classmethod
uniform(size, neuron_type=1, neuron_model='aeif_cond_alpha', neuron_param=None, syn_model='static_synapse', syn_param=None, parent=None, meta_groups=None)[source]# Make a NeuralPop of identical neurons belonging to a single “default” group.
Changed in version 1.2: Added neuron_type and meta_groups parameters
Parameters: - size (int) – Number of neurons in the population.
- neuron_type (int, optional (default: 1)) – Type of the neurons in the population: 1 for excitatory or -1 for inhibitory.
- neuron_model (str, optional (default: default neuron model)) – Neuronal model for the simulator.
- neuron_param (dict, optional (default: default neuron parameters)) – Parameters associated to neuron_model.
- syn_model (str, optional (default: default static synapse)) – Synapse model for the simulator.
- syn_param (dict, optional (default: default synaptic parameters)) – Parameters associated to syn_model.
- parent (
Graphobject, optional (default: None)) – Parent graph described by the population. - meta_groups (list or dict of str/
NeuralGroupitems) – Set of groups which can overlap: a neuron can belong to several different meta groups, i.e. they do no need to be disjoint. If all meta-groups have a name, they can be passed directly through a list; otherwise a dict is necessary.
- has_models –
-
class
nngt.SpatialGraph(nodes=0, name='SpatialGraph', weighted=True, directed=True, from_graph=None, shape=None, positions=None, **kwargs)[source]# The detailed class that inherits from
Graphand implements additional properties to describe spatial graphs (i.e. graph where the structure is embedded in space.Initialize SpatialClass instance.
Parameters: - nodes (int, optional (default: 0)) – Number of nodes in the graph.
- name (string, optional (default: “Graph”)) – The name of this
Graphinstance. - weighted (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the graph edges have weight properties.
- directed (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the graph is directed or undirected.
- shape (
Shape, optional (default: None)) – Shape of the neurons’ environment (None leads to a square of side 1 cm) - positions (
numpy.array(N, 2), optional (default: None)) – Positions of the neurons; if not specified and nodes is not 0, then neurons will be reparted at random inside theShapeobject of the instance. - **kwargs (keyword arguments for
Graphor) –Shapeif no shape was given.
Returns: self (
SpatialGraph)-
get_positions(nodes=None)[source]# Returns a copy of the nodes’ positions as a (N, 2) array.
Parameters: nodes (int or array-like, optional (default: all nodes)) – List of the nodes for which the position should be returned.
-
set_positions(positions, nodes=None)[source]# Set the nodes’ positions as a (N, 2) array.
Parameters: - positions (array-like) – List of positions, of shape (N, 2).
- nodes (int or array-like, optional (default: all nodes)) – List of the nodes for which the position should be set.
-
shape# The environment’s spatial structure.
-
class
nngt.SpatialNetwork(population, name='SpatialNetwork', weighted=True, directed=True, shape=None, from_graph=None, positions=None, **kwargs)[source]# Class that inherits from
NetworkandSpatialGraphto provide a detailed description of a real neural network in space, i.e. with positions and biological properties to interact with NEST.Initialize SpatialNetwork instance
Parameters: - name (string, optional (default: “Graph”)) – The name of this
Graphinstance. - weighted (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the graph edges have weight properties.
- directed (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the graph is directed or undirected.
- shape (
Shape, optional (default: None)) – Shape of the neurons’ environment (None leads to a square of side 1 cm) - positions (
numpy.array, optional (default: None)) – Positions of the neurons; if not specified and nodes != 0, then neurons will be reparted at random inside theShapeobject of the instance. - population (class:~nngt.NeuralPop, optional (default: None)) – Population from which the network will be built.
Returns: self (
SpatialNetwork)-
set_types(syn_type, nodes=None, fraction=None)[source]# Set the synaptic/connection types.
Changed in version 2.0: Changed syn_type to edge_type.
Warning
The special “type” attribute cannot be modified when using graphs that inherit from the
Networkclass. This is because for biological networks, neurons make only one kind of synapse, which is determined by thenngt.NeuralGroupthey belong to.Parameters: - edge_type (int, string, or array of ints) – Type of the connection among ‘excitatory’ (also 1) or ‘inhibitory’ (also -1).
- nodes (int, float or list, optional (default: None)) – If nodes is an int, number of nodes of the required type that will be created in the graph (all connections from inhibitory nodes are inhibitory); if it is a float, ratio of edge_type nodes in the graph; if it is a list, ids of the edge_type nodes.
- fraction (float, optional (default: None)) – Fraction of the selected edges that will be set as edge_type (if nodes is not None, it is the fraction of the specified nodes’ edges, otherwise it is the fraction of all edges in the graph).
Returns: t_list (
numpy.ndarray) – List of the types in an order that matches the edges attribute of the graph.
- name (string, optional (default: “Graph”)) – The name of this
-
class
nngt.Structure(size=None, parent=None, meta_groups=None, **kwargs)[source]# The basic class that contains groups of nodes and their properties.
Variables: Initialize Structure instance.
Parameters: - size (int, optional (default: 0)) – Number of nodes that the structure will contain.
- parent (
Network, optional (default: None)) – Network associated to this structure. - meta_groups (dict of str/
Groupitems) – Optional set of groups. Contrary to the primary groups which define the structure and must be disjoint, meta groups can overlap: a neuron can belong to several different meta groups. - **kwargs (
dict)
Returns: struct (
Structureobject.)-
add_meta_group(group, name=None, replace=False)[source]# Add an existing meta group to the structure.
Parameters: - group (
Group) – Meta group. - name (str, optional (default: group name)) – Name of the meta group.
- replace (bool, optional (default: False)) – Whether to override previous exiting meta group with same name.
Note
The name of the group is automatically updated to match the name argument.
- group (
-
add_to_group(group_name, ids)[source]# Add nodes to a specific group.
Parameters: - group_name (str or int) – Name or index of the group.
- ids (list or 1D-array) – Node ids.
-
create_group(nodes, name, properties=None, replace=False)[source]# Create a new group in the structure.
Parameters: - nodes (int or array-like) – Desired number of nodes or list of the nodes indices.
- name (str) – Name of the group.
- properties (dict, optional (default: None)) – Properties associated to the nodes in this group.
- replace (bool, optional (default: False)) – Whether to override previous exiting meta group with same name.
-
create_meta_group(nodes, name, properties=None, replace=False)[source]# Create a new meta group and add it to the structure.
Parameters: - nodes (int or array-like) – Desired number of nodes or list of the nodes indices.
- name (str) – Name of the group.
- properties (dict, optional (default: None)) – Properties associated to the nodes in this group.
- replace (bool, optional (default: False)) – Whether to override previous exiting meta group with same name.
-
classmethod
from_groups(groups, names=None, parent=None, meta_groups=None)[source]# Make a
Structureobject from a (list of)Groupobject(s).Parameters: - groups (list of
Groupobjects) – Groups that will be used to form the structure. Note that a given node can only belong to a single group, so the groups should form pairwise disjoints complementary sets. - names (list of str, optional (default: None)) – Names that can be used as keys to retreive a specific group. If not provided, keys will be the group name (if not empty) or the position of the group in groups, stored as a string. In the latter case, the first group in a structure named struct will be retreived by either struct[0] or struct[‘0’].
- parent (
Graph, optional (default: None)) – Parent if the structure is created from an exiting graph. - meta_groups (list or dict of str/
Groupitems) – Additional set of groups which can overlap: a node can belong to several different meta groups. Contrary to the primary groups, meta groups do therefore no need to be disjoint. If all meta-groups have a name, they can be passed directly through a list; otherwise a dict is necessary.
Example
For synaptic properties, if provided in syn_spec, all connections between groups will be set according to the values. Keys can be either group names or types (1 for excitatory, -1 for inhibitory). Because of this, several combination can be available for the connections between two groups. Because of this, priority is given to source (presynaptic properties), i.e. NNGT will look for the entry matching the first group name as source before looking for entries matching the second group name as target.
# we already created groups `g1`, `g2`, and `g3` struct = Structure.from_groups([g1, g2, g3], names=['g1', 'g2', 'g3'])
Note
If the structure is not generated from an existing
Graphand the groups do not contain explicit ids, then the ids will be generated upon structure creation: the first group, of size N0, will be associated the indices 0 to N0 - 1, the second group (size N1), will get N0 to N0 + N1 - 1, etc.- groups (list of
-
get_group(nodes, numbers=False)[source]# Return the group of the nodes.
Parameters: - nodes (int or array-like) – IDs of the nodes for which the group should be returned.
- numbers (bool, optional (default: False)) – Whether the group identifier should be returned as a number; if
False, the group names are returned.
-
get_properties(key=None, groups=None, nodes=None)[source]# Return the properties of nodes or groups of nodes in the structure.
Parameters: - groups (
str,intor array-like, optional (default:None)) – Names or numbers of the groups for which the neural properties should be returned. - nodes (int or array-like, optional (default:
None)) – IDs of the nodes for which parameters should be returned.
Returns: props (
list) – List of all dictionaries with properties.- groups (
-
ids# Return all the ids of the nodes inside the structure.
New in version 1.2.
-
is_valid# Whether the structure is consistent with the associated network.
-
meta_groups#
-
set_properties(props, nodes=None, group=None)[source]# Set the parameters of specific nodes or of a whole group.
New in version 2.2.
Parameters: - props (dict) – Dictionary containing parameters for the nodes. Entries can be either a single number (same for all nodes) or a list (one entry per nodes).
- nodes (list of ints, optional (default: None)) – Ids of the nodes whose parameters should be modified.
- group (list of strings, optional (default: None)) – List of strings containing the names of the groups whose parameters should be updated. When modifying nodes from a single group, it is still usefull to specify the group name to speed up the pace.
Note
If both nodes and group are None, all nodes will be modified.
-
size# Number of nodes in this structure.
-
nngt.generate(di_instructions, **kwargs)[source]# Generate a
Graphor one of its subclasses from adictcontaining all the relevant informations.Parameters: di_instructions ( dict) – Dictionary containing the instructions to generate the graph. It must have at least"graph_type"in its keys, with a value among"distance_rule", "erdos_renyi", "fixed_degree", "newman_watts", "price_scale_free", "random_scale_free". Depending on the type, di_instructions should also contain at least all non-optional arguments of the generator function.See also
-
nngt.get_config(key=None, detailed=False)[source]# Get the NNGT configuration as a dictionary.
Note
This function has no MPI barrier on it.
-
nngt.load_from_file(filename, fmt='auto', separator=' ', secondary=';', attributes=None, attributes_types=None, notifier='@', ignore='#', name='LoadedGraph', directed=True, cleanup=False)[source]# Load a Graph from a file.
Changed in version 2.0: Added optional attributes_types and cleanup arguments.
Warning
Support for GraphML and DOT formats are currently limited and require one of the non-default backends (DOT requires graph-tool).
Parameters: - filename (str) – The path to the file.
- fmt (str, optional (default: “neighbour”)) – The format used to save the graph. Supported formats are: “neighbour”
(neighbour list, default if format cannot be deduced automatically),
“ssp” (scipy.sparse), “edge_list” (list of all the edges in the graph,
one edge per line, represented by a
source target-pair), “gml” (gml format, default if filename ends with ‘.gml’), “graphml” (graphml format, default if filename ends with ‘.graphml’ or ‘.xml’), “dot” (dot format, default if filename ends with ‘.dot’), “gt” (only when using graph_tool`<http://graph-tool.skewed.de/>_ as library, detected if `filename ends with ‘.gt’). - separator (str, optional (default ” “)) – separator used to separate inputs in the case of custom formats (namely “neighbour” and “edge_list”)
- secondary (str, optional (default: “;”)) – Secondary separator used to separate attributes in the case of custom formats.
- attributes (list, optional (default: [])) – List of names for the attributes present in the file. If a notifier is present in the file, names will be deduced from it; otherwise the attributes will be numbered. For “edge_list”, attributes may also be present as additional columns after the source and the target.
- attributes_types (dict, optional (default: str)) – Backup information if the type of the attributes is not specified in the file. Values must be callables (types or functions) that will take the argument value as a string input and convert it to the proper type.
- notifier (str, optional (default: “@”)) – Symbol specifying the following as meaningfull information. Relevant
information are formatted
@info_name=info_value, whereinfo_nameis in (“attributes”, “directed”, “name”, “size”) and associatedinfo_valueare of type (list,bool,str,int). Additional notifiers are@type=SpatialGraph/Network/SpatialNetwork, which must be followed by the relevant notifiers among@shape,@structure, and@graph. - ignore (str, optional (default: “#”)) – Ignore lines starting with the ignore string.
- name (str, optional (default: from file information or ‘LoadedGraph’)) – The name of the graph.
- directed (bool, optional (default: from file information or True)) – Whether the graph is directed or not.
- cleanup (bool, optional (default: False)) – If true, removes nodes before the first one that appears in the edges and after the last one and renumber the nodes from 0.
Returns: graph (
Graphor subclass) – Loaded graph.
-
nngt.on_master_process()[source]# Check whether the current code is executing on the master process (rank 0) if MPI is used.
Returns: - True if rank is 0, if mpi4py is not present or if MPI is not used,
- otherwise False.
-
nngt.save_to_file(graph, filename, fmt='auto', separator=' ', secondary=';', attributes=None, notifier='@')[source]# Save a graph to file.
@todo: implement dot, xml/graphml, and gt formats
Parameters: - graph (
Graphor subclass) – Graph to save. - filename (str) – The path to the file.
- fmt (str, optional (default: “auto”)) – The format used to save the graph. Supported formats are: “neighbour”
(neighbour list, default if format cannot be deduced automatically),
“ssp” (scipy.sparse), “edge_list” (list of all the edges in the graph,
one edge per line, represented by a
source target-pair), “gml” (gml format, default if filename ends with ‘.gml’), “graphml” (graphml format, default if filename ends with ‘.graphml’ or ‘.xml’), “dot” (dot format, default if filename ends with ‘.dot’), “gt” (only when using graph_tool as library, detected if filename ends with ‘.gt’). - separator (str, optional (default ” “)) – separator used to separate inputs in the case of custom formats (namely “neighbour” and “edge_list”)
- secondary (str, optional (default: “;”)) – Secondary separator used to separate attributes in the case of custom formats.
- attributes (list, optional (default:
None)) – List of names for the edge attributes present in the graph that will be saved to disk; by default (None), all attributes will be saved. - notifier (str, optional (default: “@”)) – Symbol specifying the following as meaningfull information. Relevant
information are formatted
@info_name=info_value, withinfo_namein (“attributes”, “attr_types”, “directed”, “name”, “size”). Additional notifiers are@type=SpatialGraph/Network/SpatialNetwork, which are followed by the relevant notifiers among@shape,@structure, and@graphto separate the sections.
Note
Positions are saved as bytes by
numpy.nparray.tostring()- graph (
-
nngt.seed(msd=None, seeds=None)[source]# Seed the random generator used by NNGT (i.e. the numpy RandomState: for details, see
numpy.random.RandomState).Parameters: - msd (int, optional) – Master seed for numpy RandomState. Must be convertible to 32-bit unsigned integers.
- seeds (list of ints, optional) – Seeds for RandomState (when using MPI). Must be convertible to 32-bit unsigned integers, one entry per MPI process.
-
nngt.set_config(config, value=None, silent=False)[source]# Set NNGT’s configuration.
Parameters: - config (dict or str) – Either a full configuration dictionary or one key to be set together with its associated value.
- value (object, optional (default: None)) – Value associated to config if config is a key.
Examples
>>> nngt.set_config({'multithreading': True, 'omp': 4}) >>> nngt.set_config('multithreading', False)
Notes
See the config file nngt/nngt.conf.default or ~/.nngt/nngt.conf for details about your configuration.
This function has an MPI barrier on it, so it must always be called on all processes.
See also
-
nngt.use_backend(backend, reloading=True, silent=False)[source]# Allows the user to switch to a specific graph library as backend.
Warning
If
Graphobjects have already been created, they will no longer be compatible with NNGT methods.Parameters: - backend (string) – Name of a graph library among ‘graph_tool’, ‘igraph’, ‘networkx’, or ‘nngt’.
- reloading (bool, optional (default: True)) – Whether the graph objects should be reloaded through reload (this should always be set to True except when NNGT is first initiated!)
- silent (bool, optional (default: False)) – Whether the changes made to the configuration should be logged at the DEBUG (True) or INFO (False) level.